What is offline data storage?
Offline data storage is a secure way to store and access archival or permanent data. Data is not transmitted over a network and therefore cannot be intercepted over the wire. Another attribute of offline storage is that it is removeable. The data stored in offline storage remains permanent when it is disconnected from the computer or environment. Offline data storage provides an air-gap security capability between connected online data environments and disconnected environments to safeguard against ransomware, hacking, and disasters. After all, it is never a good idea to put all your eggs into one big open basket.
What does offline data storage involve?
Offline data storage consists of any method and storage medium that does not connect to a network and cannot be accessed through a communications network. This includes creating duplicate copies of data on different storage technologies, distributing the data to different locations, protecting data integrity, and the migration of data for long-term preservation.
Offline data storage offers organizations the ability to diversify their storage capabilities according to user needs, application priorities, improved resource management, and security. This diversification enables data center and storage administrators to deploy a hierarchal storage device environment consisting of 4 levels: primary, secondary, tertiary, and offline. Traditional storage architects define secondary storage as a device that retains memory if power is lost. However, technology and its economic needs are changing so it makes sense to categorize the levels and types of storage by its purpose and value for an organization.
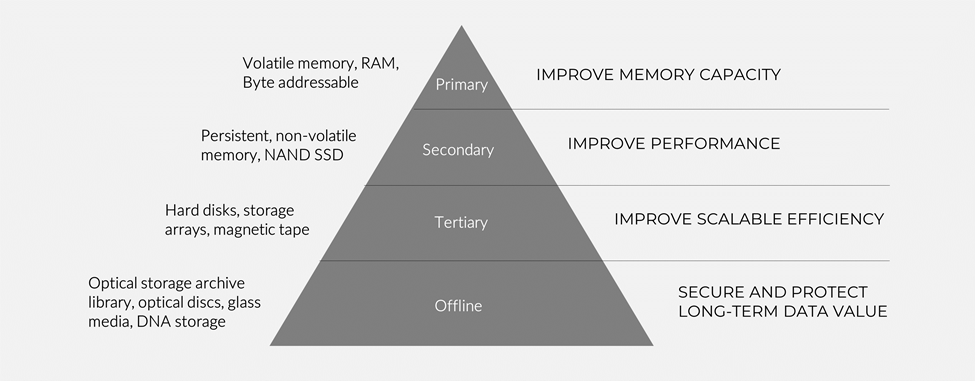
Figure 1: Modern storage device hierarchy
Organizations can build large in-house data storage systems that are not connected to the outside world. Access to the offline storage systems is therefore controlled to serve the needs of its on-prem users, while isolating its data from any outside access. Added assurances of data integrity are made through WORM storage (write-once, read only. LINK- READ MORE HERE).
The good and the bad with networks is that it connects computers and storage environments together to allow data to flow between them, however, this data flow creates doorways between these environments. The ultimate security is to eliminate doorways. When that is the case, offline data storage can be used in ways to allow secure local read/write access to shared data.
What are the benefits of offline storage?
- Save network data transfer fees and costs
Physical transport of large quantities of data will continue to play an important role in the dissemination of information. When using a communications network to stream data, transfer costs can build very quickly. Transferring terabytes and petabytes of data through cloud service providers incurs egress or interconnection fees, and regional bandwidth fees, as well as additional costs if you choose to rent a dedicated line. The bandwidth alone to transfer 2 petabytes of data would roughly cost over $100K depending on location. It would also take a year to transfer the data at a speed of 400Mbps – considering no errors. In some cases, it would save more time and money to ship the data to the location.
- Reduce risk from disasters
Reducing the risk of downtime from data loss is a key imperative for any organization. IT managers can backup local data into a cloud storage container, migrate the data onto optical media, store optical archives into offsite storage facility, and restore the data anytime through the container. This provides a method for duplicating and moving data to different locations and technologies in the case of the need to recover data from a data loss incident.
- Preserving digital assets for future value
Efficiently storing, organizing, managing, retrieving, and distributing an organization’s digital assets is vital to increasing the value of data and its usefulness – especially when data must be preserved for the long-term such as:
- Any digital asset that includes the right to use
- Non-fungible tokens
- Brand and marketing assets
- Records
- Documents
- Images
- Audio content
- Video
- Animations
- Media files
- Graphics
- Presentations
Digital asset lifecycle management goes through the entire process of creating, managing, storing, retrieving, archiving, and protecting digital assets. Since digital assets may not be frequently accessed, offline data storage such as optical libraries provide the lowest cost option to store, secure, protect, and retrieve digital assets.
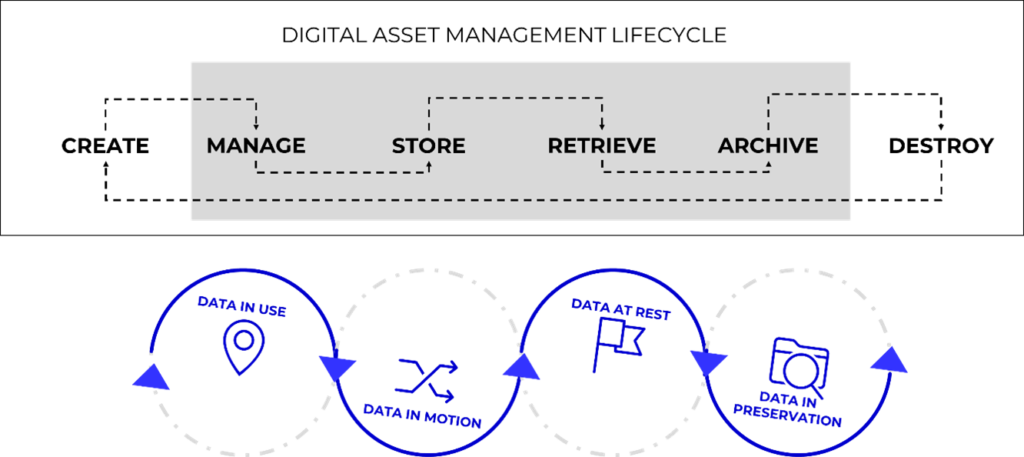
Figure 2. Digital asset management lifecycle. The movement of offline data increases the value of data.

